개인 프로젝트/시스템트레이딩
[affinity propagation] GraphicalLassoCV 를 이용한 비지도 군집화
달죽
2020. 11. 10. 10:25
반응형
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
from sklearn import cluster, covariance, manifold
import sys
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
print(__doc__)
quotes = []
import FinanceDataReader as fdr # 주가데이터 불러오는 모듈
data = pd.read_csv('sector_2020-11-05.csv').iloc[:100].dropna(axis=0)CODE = data.CODE.tolist()
names = data.CODE_NAME.tolist()
quotes = []
for i in CODE :
d = fdr.DataReader(i, "20180830", "20201106").reset_index()[['Date','Open','Close']]
quotes.append(d)
quotes[0].Close
537일 동안의 종가 데이터를 불러온것.
close_prices = np.vstack([q['Close'] for q in quotes])
open_prices = np.vstack([q['Open'] for q in quotes])
# 하루의 변동성을 추출해온다.
variation = close_prices - open_prices
# #############################################################################
edge_model = covariance.GraphicalLassoCV()
# covariance 를 distance 로 설정하기 위해 이 모델을 불러온다.
# 시계열 정규화 : covariance 공분산보다 correlation 상관계수를 이용하는게
# 구조를 만들때 더 효과적이다.
X = variation.copy().T
X = np.array(X,dtype=float)
names = np.array(names)
X.shape
# (538, 82)X /= X.std(axis=0)
edge_model.fit(X)
# #############################################################################
# affinity propagation 를 이용해 군집화 해보자.
_, labels = cluster.affinity_propagation(edge_model.covariance_,
random_state=0)
n_labels = labels.max()
for i in range(n_labels + 1):
print('Cluster %i: %s' % ((i + 1), ', '.join(names[labels == i])))
# #############################################################################
# 시각화를 위한 저차원 임베딩 찾기: 2D 평면에서 노드에서의 최상의 위치를 찾습니다
# 우리는 재현성을 달성하기 위해 밀도가 높은 eigen_solver 를 사용한다
# arpack은 우리가 통제하지 않는 무작위 벡터로 시작된다
# 우리는 대규모 구조를 포착하기 위해 많은 이웃을 사용한다.
node_position_model = manifold.LocallyLinearEmbedding(
n_components=2, eigen_solver='dense', n_neighbors=6)
embedding = node_position_model.fit_transform(X.T).T
# #############################################################################
# 시각화
plt.figure(1, facecolor='w', figsize=(10, 8))
plt.clf()
ax = plt.axes([0., 0., 1., 1.])
plt.axis('off')
# partial correlations 그래프 시각화
partial_correlations = edge_model.precision_.copy()
d = 1 / np.sqrt(np.diag(partial_correlations))
partial_correlations *= d
partial_correlations *= d[:, np.newaxis]
non_zero = (np.abs(np.triu(partial_correlations, k=1)) > 0.02)
# 임베딩의 좌표를 사용하여 노드를 배치합니다
plt.scatter(embedding[0], embedding[1], s=100 * d ** 2, c=labels,
cmap=plt.cm.nipy_spectral)
# 가장자리 그래프를 그려줍니다.
start_idx, end_idx = np.where(non_zero)
# (*line0*, *line1*, *line2*)
# linen = (x0, y0), (x1, y1), ... (xm, ym)
segments = [[embedding[:, start], embedding[:, stop]]
for start, stop in zip(start_idx, end_idx)]
values = np.abs(partial_correlations[non_zero])
lc = LineCollection(segments,
zorder=0, cmap=plt.cm.hot_r,
norm=plt.Normalize(0, .7 * values.max()))
lc.set_array(values)
lc.set_linewidths(15 * values)
ax.add_collection(lc)
path = 'C:\\Users\\user\\Downloads\\NEXONLv1GothicLight.ttf' # 글자 깨지기 방지
fontprop = fm.FontProperties(fname=path, size=8)
# Add a label to each node. The challenge here is that we want to
# position the labels to avoid overlap with other labels
for index, (name, label, (x, y)) in enumerate(
zip(names, labels, embedding.T)):
dx = x - embedding[0]
dx[index] = 1
dy = y - embedding[1]
dy[index] = 1
this_dx = dx[np.argmin(np.abs(dy))]
this_dy = dy[np.argmin(np.abs(dx))]
if this_dx > 0:
horizontalalignment = 'left'
x = x + .002
else:
horizontalalignment = 'right'
x = x - .002
if this_dy > 0:
verticalalignment = 'bottom'
y = y + .002
else:
verticalalignment = 'top'
y = y - .002
plt.text(x, y, name, size=12,
horizontalalignment=horizontalalignment,
verticalalignment=verticalalignment,
fontproperties=fontprop,
bbox=dict(facecolor='w',
edgecolor=plt.cm.nipy_spectral(label / float(n_labels)),
alpha=.6))
plt.xlim(embedding[0].min() - .15 * embedding[0].ptp(),
embedding[0].max() + .10 * embedding[0].ptp(),)
plt.ylim(embedding[1].min() - .03 * embedding[1].ptp(),
embedding[1].max() + .03 * embedding[1].ptp())
plt.show()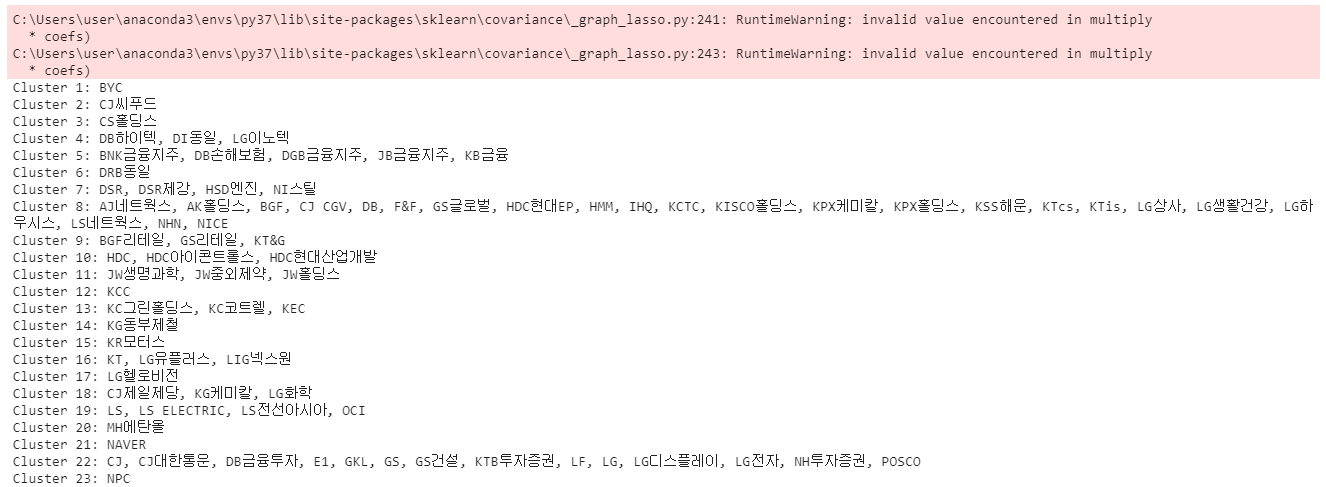
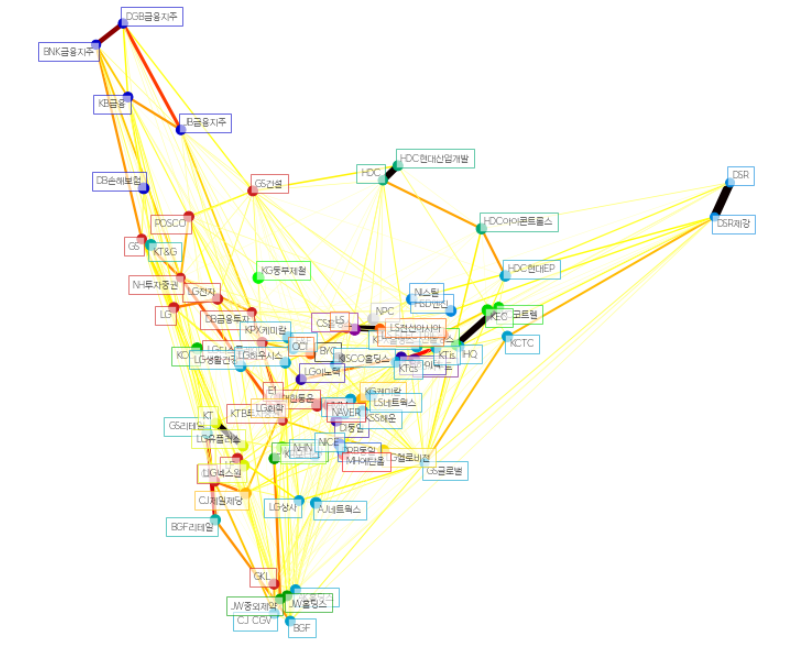
2년간의 종목의 종가만으로 어떤 종목들이 서로 주가상관성을 이루고 있는지 군집화를 보여주는 그래프다.
보통 같은 계열사, 같은 업종이 같이 움직이는것을 한눈에 볼수 있다.
K-means 도 시계열의 correlation 을 distance 로 구현해볼수 있는데, k-means 는 군집수를 정해줘야 한다.
다음에는 k-means를 이용해서 시계열 데이터를 이용해 군집화를 해보겠다.

반응형